realizată de Lippa-Braganza Sebastian 3 luni în urmă
33
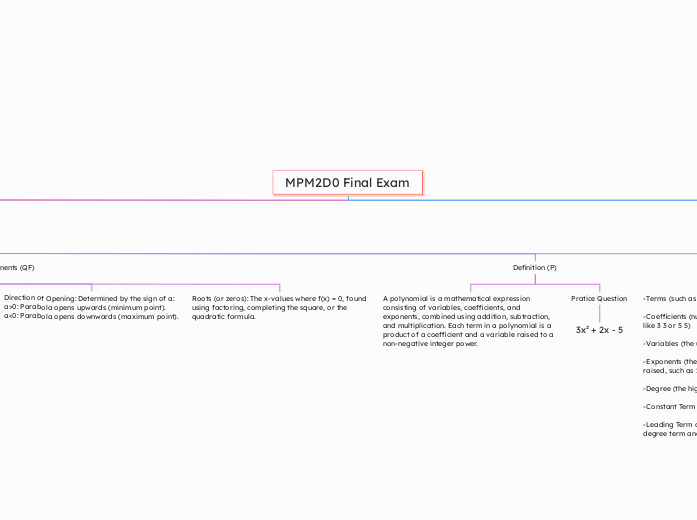
MPM2D0 Final Exam
Linear systems involve solving multiple linear equations simultaneously to find common values for the variables, typically represented as points of intersection. These systems can yield a unique solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions, depending on the nature of the lines involved.