by Ruth Ruth 1 month ago
71
More like this
H+ Pump- transport of protons against their concentration gradient
Intra Cellular moecule- nonpolar and can diffuse through the plasma membrane, therefore molecule binds to the receptor in the cell
Membrane Molecule- Polar molecule /large molecule that can't pass the plasma membrane
Reception, Transduction, Response- Reception is when the molecule binds to the receptor. Transduction is the process of transferring signals throughout an organism. Response is the action that occurs due to the activation of kinase and ATP, and other molecules making a cellular response
Ion Channel Receptor- Ion channels are closed, then a signal molecule binds to the receptor causing the channels to change shape and open. Ions start to flow through until the molecule unbinds, and the channels close
GPCR Signaling- First a polar signaling molecule binds to the inactive GPCR and activates it. Then the G-protein activates which leads to the binding of G protein to the GPCR making the G protein change its shape and kick GDP off and becomes GTP. GTP then slides over to Adenylyl Cyclase and binds to it activating it and it alters it shape, while also becoming GDP again by kicking off a phosphate group with Phosphatases. Then Adenylyl Cyclase turns ATP into cAMP, which then cAMP activate a protein kinase, creating a cellular response.
.Phosphorylation cascade is an example of signal transduction pathway that uses Kinases and Phosphatases.
Adenylyl Cyclases- Enzyme that is used to activate the second messenger cAMP
Protein Kinases: (Adds phosphate groups)Enzymes that catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to proteins
Phosphatases-( Removes phosphate groups)an enzyme that removes a phosphate group from proteins
Second messengers- are small, nonprotein, water-soluble molecules or ions that are used in signal transduction to relay a signal within a cell (They are synthesized or released by specific enzymatic reactions, usually as a result of an external signal that was received by a transmembrane receptor and pre-processed by other membrane-associated proteins)
Steroid Hormone Siglaning- the signal molecule is nonpolar so it can diffuse through the plasma membrane, and binds to the receptor inside. Then the receptor goes into the nucleus and taps DNA, which then DNA does transcription of mRNA. The mRNA then leaves the nucleus and is translated into a specific protein
Acidic amino acids
Negatively Charged
Basic amino acids
Positively charged
Nonpolar amino acids
Heating a protein up will denature (unfold) the protein to a straight line.
Secondary structure- Folding is beginning to happen it can either be alpha helix or beta pleated sheet. The folding depends on the sequence of the amino acids. Both of these are due to the hydrogen bonds.
Tertiary groups- The folding continues and is folding the secondary structures. Interactions begin between the r groups. The r groups can vary and depending on the r groups depends on the folding of the protein.
Quaternary structure- There are more than 2 polypeptides folded together. Interactions are by the R groups
If there are hydrophobic interactions the protein would fold inwards letting the hydrophobic interact on the inside with other hydrophobic r groups. The hydrophilic interactions would be outwards interacting with other hydrophilic r groups.
The R-group interactions are hydrophobic, hydrophillic, disulfide, van der waals, ionic, and hydrogen bonds.
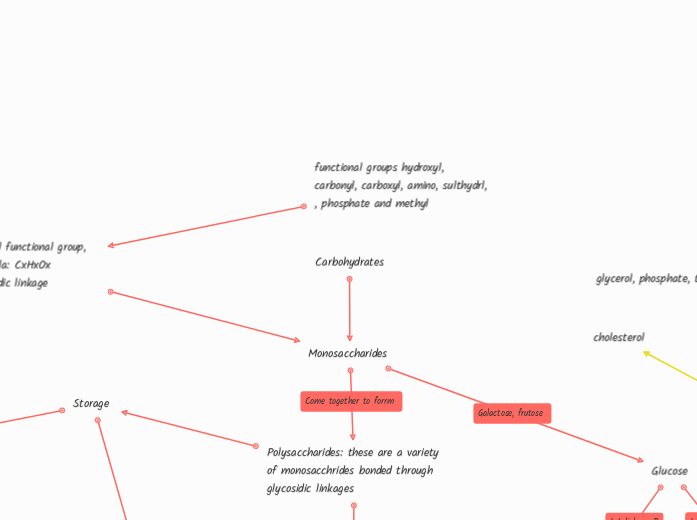
Beta Glucose
Same chemical formula, different structure arrangement of OH
Cannot be broken down by enzymes
Alpha Glucose
Can be broken down by enzymes
Storage
Glycogen: animals
1-6 Glycosidic linkage
Alpha Glucose, 1-4 glycosidic linkage, branching, easy to break
Starch: plants
Amylopectin
Branching, Alpha glucose, 1-4 glycosidic linkage, can be easily broken
Amylose
No branching, Alpha glucose, 1-4 glycosidic linkage, cannot be easily broken
Helical shaped
Structure
Cellulose
Beta glucose, 1-4 beta glycosidic linkage, no branching, Plant cell